Types of Home Insulation
-
Table of Contents
Home insulation is a critical component in maintaining energy efficiency, comfort, and cost-effectiveness in residential buildings. Various types of insulation materials and methods are available, each with unique properties and applications suited to different areas of a home. The primary types of home insulation include fiberglass, cellulose, spray foam, rigid foam, and mineral wool. Fiberglass insulation, available in batts or loose-fill, is widely used for its affordability and ease of installation. Cellulose insulation, made from recycled paper products, offers excellent thermal performance and environmental benefits. Spray foam insulation provides superior air sealing and high R-values, making it ideal for hard-to-reach areas. Rigid foam insulation, available in panels, is used for its high insulating value and moisture resistance. Mineral wool insulation, known for its fire resistance and soundproofing qualities, is another versatile option. Understanding the characteristics and best uses of each type of insulation can help homeowners make informed decisions to enhance their home’s energy efficiency and comfort.
Benefits Of Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation has emerged as a popular choice among homeowners and builders due to its numerous benefits. This type of insulation, which is applied as a liquid and then expands into a foam, offers several advantages that make it a superior option compared to traditional insulation materials like fiberglass or cellulose. One of the primary benefits of spray foam insulation is its exceptional thermal performance. The foam creates an airtight seal that significantly reduces heat transfer, thereby enhancing the energy efficiency of a home. This reduction in heat loss and gain translates to lower energy bills, as heating and cooling systems do not have to work as hard to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
In addition to its thermal properties, spray foam insulation also excels in providing a high level of moisture resistance. Unlike other insulation materials that can absorb water and become less effective, spray foam maintains its insulating properties even when exposed to moisture. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in areas prone to high humidity or water intrusion, as it helps prevent mold growth and structural damage. Consequently, homeowners can enjoy a healthier living environment and potentially lower maintenance costs over time.
Another significant advantage of spray foam insulation is its ability to improve indoor air quality. The airtight seal created by the foam minimizes the infiltration of outdoor pollutants, allergens, and dust, which can contribute to respiratory issues and other health problems. By reducing the entry of these contaminants, spray foam insulation helps create a cleaner and healthier indoor environment. Furthermore, the foam’s ability to fill even the smallest gaps and cracks ensures that there are no hidden spaces where pests can enter and nest, thereby contributing to a pest-free home.
The durability and longevity of spray foam insulation are also noteworthy. Once applied, the foam hardens and retains its shape and insulating properties for many years, often outlasting other types of insulation. This long-term performance means that homeowners do not have to worry about frequent replacements or degradation of the insulation material. Additionally, spray foam insulation can add structural strength to walls and roofs, providing an extra layer of protection against external forces such as wind and seismic activity.
Moreover, spray foam insulation is versatile and can be used in various parts of a home, including walls, roofs, attics, and crawl spaces. Its ability to conform to irregular shapes and hard-to-reach areas makes it an ideal solution for both new construction and retrofitting existing structures. This versatility ensures that every part of the home is adequately insulated, contributing to overall energy efficiency and comfort.
While the initial cost of spray foam insulation may be higher than that of traditional insulation materials, the long-term savings on energy bills and maintenance costs can offset this initial investment. Additionally, many homeowners may qualify for tax credits or rebates for installing energy-efficient insulation, further reducing the overall cost.
In conclusion, the benefits of spray foam insulation are manifold, ranging from superior thermal performance and moisture resistance to improved indoor air quality and durability. Its ability to create an airtight seal, fill gaps and cracks, and add structural strength makes it a highly effective and versatile insulation solution. Although the upfront cost may be higher, the long-term advantages make spray foam insulation a worthwhile investment for homeowners seeking to enhance the energy efficiency, comfort, and longevity of their homes.
Comparing Fiberglass And Cellulose Insulation
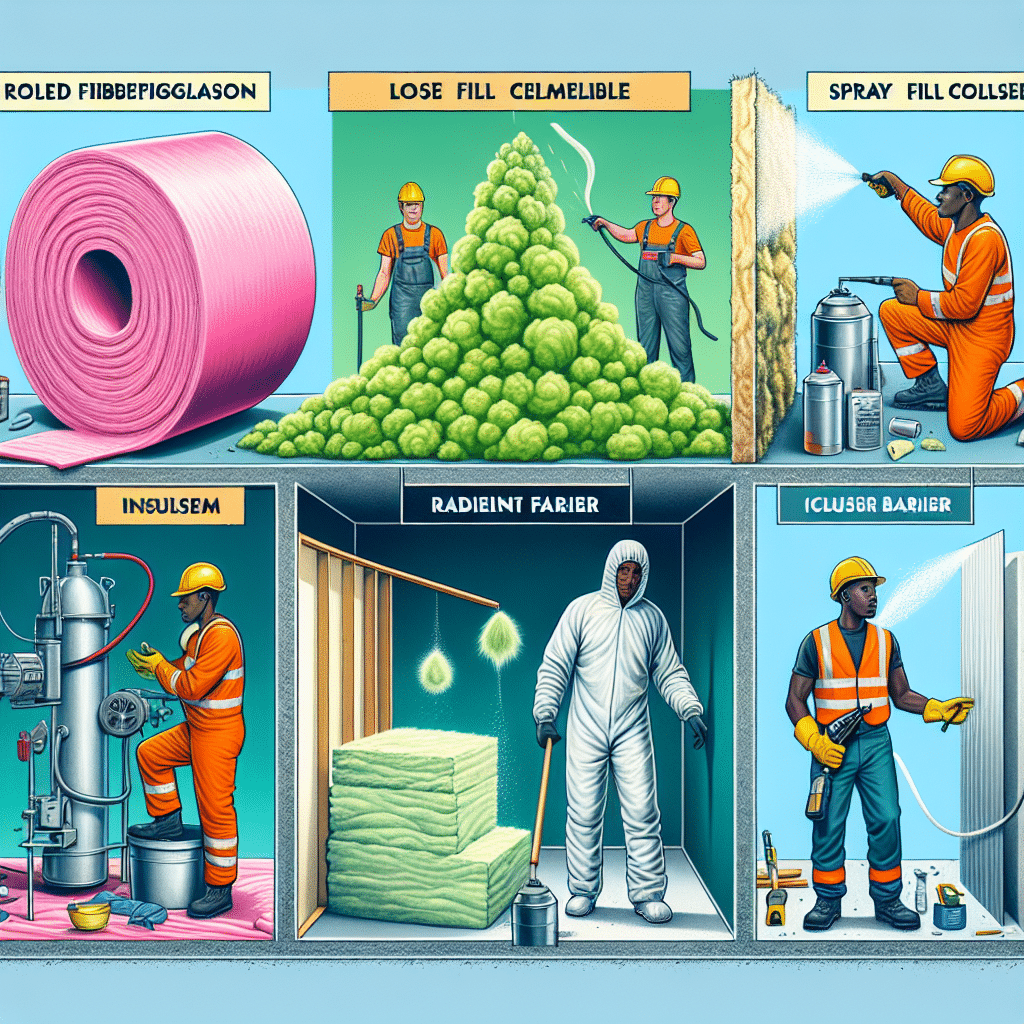
When considering home insulation options, homeowners often find themselves comparing fiberglass and cellulose insulation. Both materials are widely used and offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand their characteristics to make an informed decision.
Fiberglass insulation, composed of fine glass fibers, is one of the most common types of insulation. It is available in various forms, including batts, rolls, and loose-fill. One of the primary benefits of fiberglass insulation is its thermal performance. It has a high R-value, which measures the material’s resistance to heat flow, making it effective in maintaining indoor temperatures. Additionally, fiberglass is non-combustible, providing an added layer of fire safety. Its resistance to moisture also helps prevent mold growth, contributing to a healthier indoor environment.
On the other hand, cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper products, primarily newsprint, treated with fire-retardant chemicals. This eco-friendly option is often praised for its sustainability. Cellulose insulation is typically installed as loose-fill, blown into wall cavities, attics, and other spaces. One of the notable advantages of cellulose is its ability to conform to irregular spaces and fill gaps more effectively than fiberglass batts. This characteristic enhances its thermal performance by reducing air leakage and improving energy efficiency.
Despite these benefits, each type of insulation has its drawbacks. Fiberglass insulation, while effective, can be irritating to the skin and respiratory system during installation. Proper protective gear is necessary to avoid discomfort and potential health risks. Moreover, fiberglass batts must be installed meticulously to avoid gaps and compression, which can significantly reduce their effectiveness. In contrast, cellulose insulation, although easier to install in some respects, can settle over time, potentially leading to reduced insulation performance. This settling can create voids and reduce the material’s overall R-value.
Another critical factor to consider is the environmental impact of each insulation type. Fiberglass insulation, although durable, is not biodegradable and can contribute to landfill waste at the end of its life cycle. Conversely, cellulose insulation is made from recycled materials and is biodegradable, making it a more environmentally friendly option. However, the chemicals used to treat cellulose for fire resistance can raise concerns about indoor air quality and potential health effects.
Cost is another consideration for homeowners. Generally, fiberglass insulation tends to be less expensive than cellulose insulation. The lower initial cost can make fiberglass an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. However, the long-term energy savings provided by cellulose insulation’s superior air-sealing capabilities may offset the higher upfront cost over time.
In terms of soundproofing, cellulose insulation has an edge over fiberglass. Its dense composition helps to dampen sound transmission, making it a better choice for reducing noise between rooms or from external sources. This characteristic can be particularly beneficial in urban areas or multi-family dwellings where noise reduction is a priority.
Ultimately, the choice between fiberglass and cellulose insulation depends on various factors, including budget, environmental considerations, installation preferences, and specific performance needs. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of each material, homeowners can select the insulation type that best suits their requirements, ensuring a comfortable and energy-efficient living space.
Eco-Friendly Insulation Options For Modern Homes
In the quest for sustainable living, eco-friendly insulation options have become increasingly significant for modern homes. As homeowners and builders seek to reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental impact, understanding the various types of eco-friendly insulation available is crucial. These options not only contribute to a greener planet but also offer numerous benefits in terms of energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
One of the most popular eco-friendly insulation materials is cellulose. Made primarily from recycled paper products, such as newspapers, cellulose insulation is treated with non-toxic fire retardants to enhance its safety. This material is highly effective in reducing heat transfer, thereby maintaining a stable indoor temperature and lowering energy bills. Additionally, cellulose insulation is biodegradable and has a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional fiberglass insulation, making it an excellent choice for environmentally conscious homeowners.
Another sustainable option is sheep’s wool insulation. This natural material is not only renewable but also boasts impressive insulating properties. Sheep’s wool can absorb and release moisture without compromising its insulating ability, which helps regulate indoor humidity levels. Furthermore, it is naturally fire-resistant and has the added benefit of being able to filter indoor air by trapping pollutants. The use of sheep’s wool insulation supports sustainable farming practices and reduces reliance on synthetic materials.
Cotton insulation, often derived from recycled denim, is another eco-friendly alternative. This material is treated with boric acid to enhance its fire resistance and pest-repellent properties. Cotton insulation is non-toxic, easy to handle, and provides excellent thermal and acoustic insulation. By repurposing discarded denim, this insulation option helps reduce landfill waste and promotes recycling efforts.
In addition to these natural materials, there are also innovative options like spray foam insulation made from soy-based products. Traditional spray foam insulation is known for its high insulating value and ability to seal gaps and cracks effectively. However, soy-based spray foam offers the same benefits while being derived from a renewable resource. This type of insulation reduces the reliance on petroleum-based products and contributes to a lower carbon footprint.
Moreover, rigid foam boards made from recycled polystyrene are gaining popularity as an eco-friendly insulation choice. These boards are manufactured using post-consumer and post-industrial waste, which helps divert plastic from landfills. Rigid foam boards provide excellent thermal resistance and are particularly useful for insulating foundations, walls, and roofs. Their durability and moisture resistance make them a long-lasting and sustainable option for modern homes.
Transitioning to eco-friendly insulation options not only benefits the environment but also enhances the overall health and comfort of a home. Many of these materials have superior air quality benefits, as they do not release harmful chemicals or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the indoor environment. This is particularly important for individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions, as it contributes to a healthier living space.
In conclusion, the variety of eco-friendly insulation options available today allows homeowners to make informed choices that align with their sustainability goals. From cellulose and sheep’s wool to cotton and soy-based spray foam, each material offers unique advantages that contribute to energy efficiency and environmental preservation. By opting for these sustainable insulation solutions, modern homes can achieve a balance between comfort, cost savings, and ecological responsibility.
Read more about Home Insulation
- Benefits of Home Insulation
- Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Home
- Common DIY Home Insulation Mistakes
- Insulation for Different Areas of Your Home
- Signs of Poor Home Insulation
- Home Insulation ROI (Return on Investment)
- How to Improve Home Insulation without Breaking the Bank
- Upgrading Home Insulation for Extreme Climates
- Maintaining and Updating Home Insulation








